Research
<日本語/English>
![]()
Metal complexes have structural and electronic flexibilities which respond to external stimulus such as light, heating and guest, leading tothe development of future sensor, memory devices and molecular actuators. Our group are investigating switchable physical properties of spin crossover (spin transition) Fe(II/III) and Co(II) complexes, and coordination polymers responding to the external stimulus.
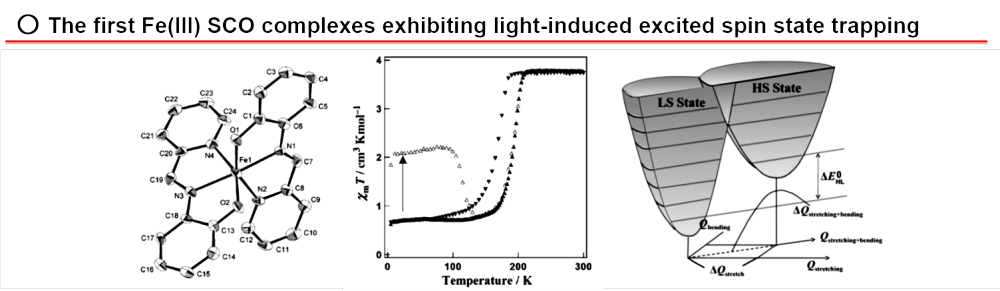
○ Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 3497-3508
○ J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 7126-7127.
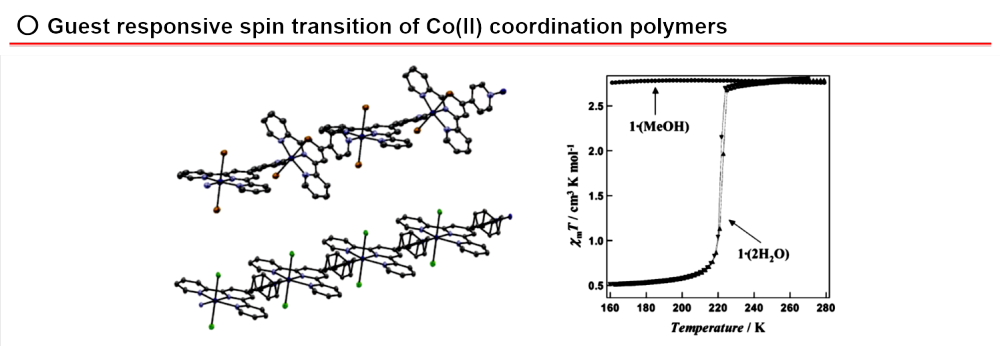
○ Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 4124-4126.
○ J. Mater. Chem. C. 2015, 3, 7865-7869.
○ Dalton. Trans. 2021, 50, 7843-7853.
![]()
Soft materials incoporating long alkyl chains show unipue properties such
as phase transition and liquid crystalline property based on their structural
flexibility. Our group are developing multi-functional soft materials exhibiting
structural flexibility yogether with electronic properties by introducing
alkyl chains into metal complex cores.
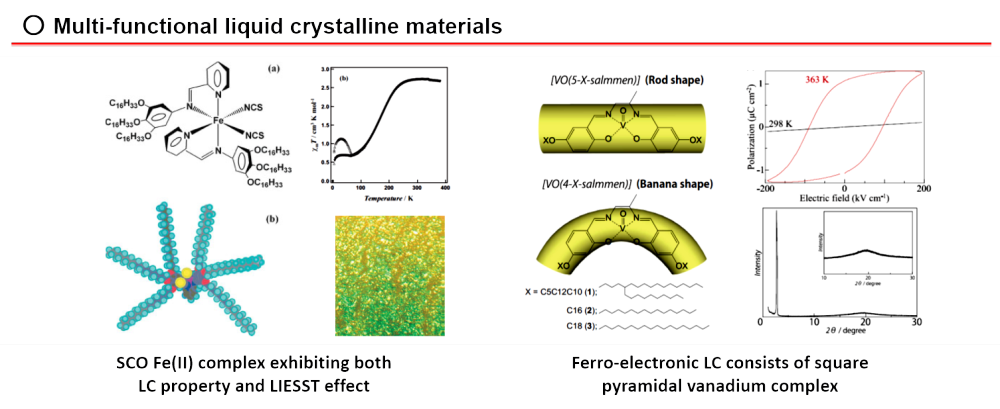
○ Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 869-872.
○ Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 7295-7297.
○ Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 7692-7694.
○ Polyhedron 2007, 26, 2375-2380.
○ Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2011, 14, 1498-1500.
○ Polyhedron 2011, 30, 3001-3005.
○ Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2012, 16, 89-91.
○ J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2013, 23, 186-192.
○ Sci Rep. 2015, 5, 16606.
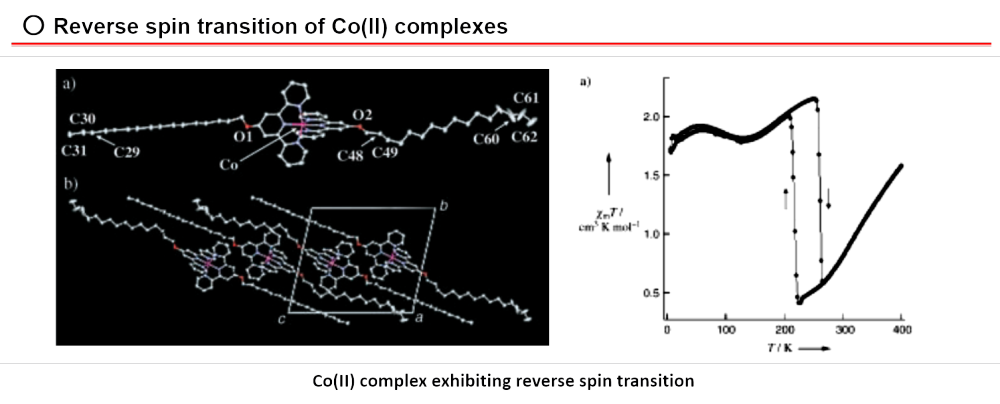
○ Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4899-4903.
○ Polyhedron 2009, 28, 2053-2057.
○ Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 1428-1432.
○ Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 2167-2169.
○ Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2769-2775.
○ Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 3332-3337.
![]()
Carbon materials have attravted much attention as the next-generation functional
materials. Our group are developing proton conductors based on the carbon
materials such as graphene oxide (GO) and carbon sphere (CS). Moreover,
we are investigating multi-functions developed by a hybridization of GO
with inorganic compounds such as metal oxides and metal complexes.
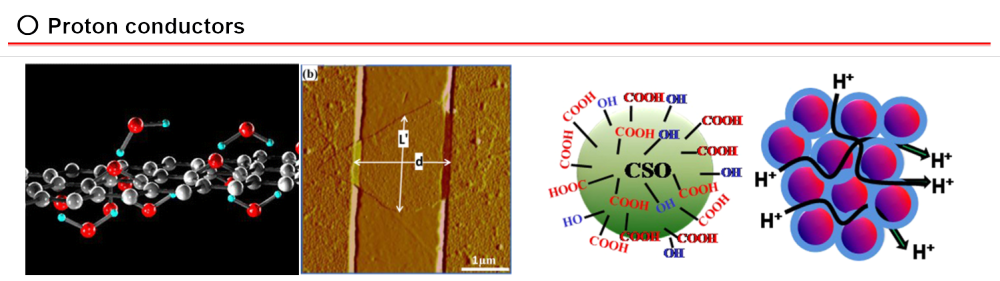
○ J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8097-8100.
○ Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6997-7000.
○ Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 2322-2327.
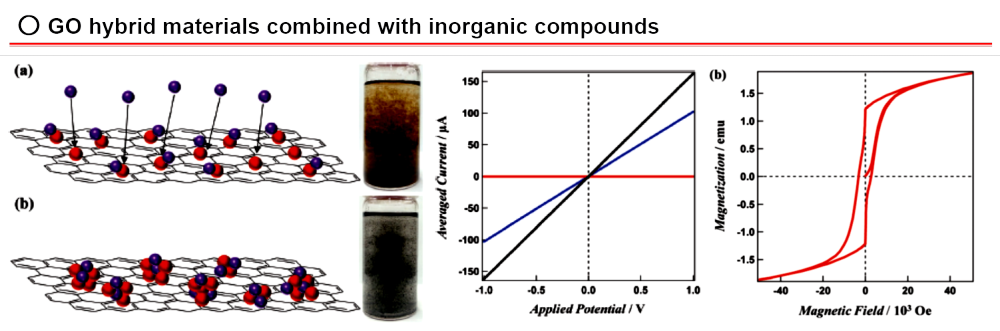
○ Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 323-332.
○ Inorg. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 886-892.
○ Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 5049-5052.
○ Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 842-848.



